CVXPY
Basics
import cvxpy as cp
x = cp.Variable()
y = cp.Variable()
constraints = [x + y == 1,
x - y >= 1]
obj = cp.Minimize((x-y)**2)
prob = cp.Problem(obj, constraints)
prob.solve()
print(prob.status)
print(prob.value)
print(x.value, y.value)
-
Status:
-
optimal (
cp.OPTIMAL)solved successfully.
-
infeasible (
cp.INFEASIBLE)eg.
Minimize(x), [x>=1, x<=0]
-
unbounded (
cp.UNBOUNDED)eg. only
Minimize(x)
-
*_inaccurate
if only get low accuracy result than desired.
-
SolverError
eg. not a DCP problem.
should try other solvers.
-
-
Variables
dimensions can be 0,1,2.
scalar = cp.Variable() vector = cp.Variable(5) # [5,] matrix = cp.Variable((2,3)) # [2,3]Numpy ndarray, Scipy sparse matrix is supported.
# Problem data. m = 10 n = 5 numpy.random.seed(1) A = numpy.random.randn(m, n) b = numpy.random.randn(m) # Construct the problem. x = cp.Variable(n) objective = cp.Minimize(cp.sum_squares(A*x - b)) constraints = [0 <= x, x <= 1] prob = cp.Problem(objective, constraints) print("Optimal value", prob.solve()) print("Optimal var") print(x.value) # A numpy ndarray.
-
Constraints
use ==, >=, <= for constraints.
semidefinite
-
Parameters
Parameter is used to change the value of a constant without rebuilding the Problem.
Can be attributed as nonpos, nonneg, ... (for DCP use)
# Positive scalar parameter. m = cp.Parameter(nonneg=True) # Column vector parameter with unknown sign (by default). c = cp.Parameter(5) # Matrix parameter with negative entries. G = cp.Parameter((4, 7), nonpos=True) # Assigns a constant value to G. G.value = -numpy.ones((4, 7)) # Create parameter, then assign value. rho = cp.Parameter(nonneg=True) rho.value = 2 # Initialize parameter with a value. rho = cp.Parameter(nonneg=True, value=2)
DCP
DCP is used to ensure the optimization problem is convex. (sufficient but not necessary)
-
Expressions
formed by
- Variable, Parameter, numerical constants (support ndarray)
+,-,*,/- cvxpy functions
Properties:
shape, size, ndim, sign, curvature- shape, size, ndim
-
sign
ZERO, UNKNOWN, NONPOSITIVE, NONNEGATIVE
-
curvature
AFFINE, CONSTANT, CONVEX, CONCAVE, UNKNOWN
-
DCP tree analysis
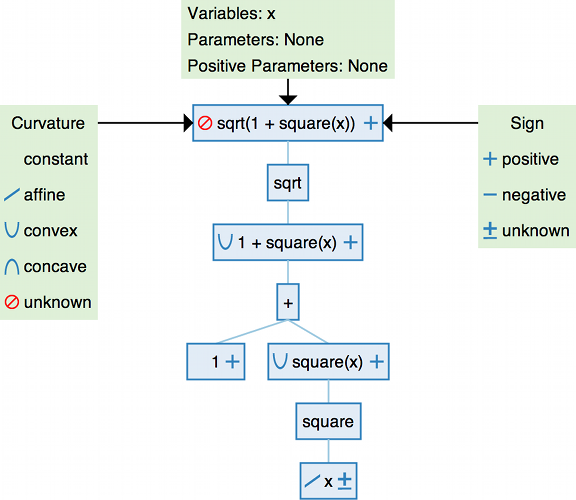
-
DCP rules
- Objectice
- Minimize(Convex)
- Maximize(Concave)
- Constraints
- affine == affine
- convex <= concave
- concave >= convex
prob.is_dcp() - Objectice
Atomic functions
Index and slice and transpose and power
like numpy
expr.T
expr**2 or power(expr, 2)
scalar functions
- max() convex
-
min() concave
consider min(concave, concave) is concave.
-
norm(X) default is 2-norm.
norm(X, 1), norm(X, "inf")
- sum_squares(X) convex
- sum(X) affine
- quad_over_lin(X, y)
- trace(X) affine
- ...
element-wise functions
- abs(x) convex
-
entr(x)
entropy,
-xlogx, concave
- exp(x), log(x)
- neg(x), pos(x), both convex
- sqrt(x), power(x)
vector/matrix functions
- reshape() affine
- diag() affine