String
char
-
偏序编码规则:
根据字符的自然定义,某些字符间两两可以比较次序。(一般为字典序)
string
-
存储
- 静态:顺序,c标准字符串。
- 动态:String类。
-
方法
-
标准字符串
char* s[L] // capacity is L-1. ('\0' is reserved for the last place.) int strlen(char* s) char* strstr(char* str1, char* str2) // find str2 in str1, if not found, return NULL char* strcpy(char* to, char* from) // return `to` char* strcat(char* to, char* from) int strcmp(char* a, char* b) // 0 for == char* strchr(char* s, char c) // find c in s (left to right), return &s[i] or '\0' char* strrchr(char* s, char c) // right to left
-
class string
string s; // empty string s2 = s.substr(start, count); // shrink count automatically s3 = s + s2; int l = s.length(); string s = string(1, 'a'); // single char to string. to_string() is wrong. string s = to_string(123); // s="123" s[0] = 'r' // mutable int a = stoi(s); // stof, stoll, stod, ... s.find(s2) // int index to s2, or -1 if not found
-
Pattern Matching
-
Classification
-
Exact Matching
Single Matching, Ambiguous (Wild-Card), Regular Expression.
-
Approximate Matching
Edit Distance: Insertion, Deletion, Replacement.
(Genomic Alignment)
-
-
Algorithms
Assuming Target length is \(n\), Pattern length is \(m\).
-
Brute Force
Time: \(O(nm)\)
int BF(string t, string p){ int i,j; for(i=0; i<t.length()-p.length(); i++){ for(j=0, j<p.length()&&t[i+j]==p[j]; j++) ; if(j==p.length()) return i; } return -1; }
-
KMP
**Time: \(O(m+n)\). **
No back-tracing match.
Why
k = next[k]: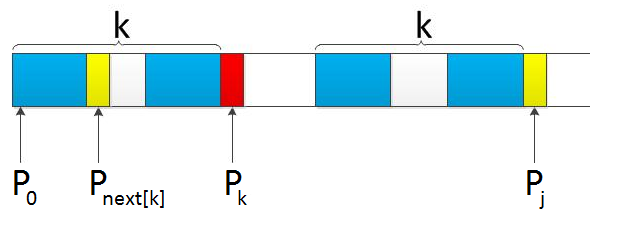
/******************************* * What is next[i] ? * length of Longest Commen Prefix & Postfix of [0,i-1] * 可以重叠,但不能完全重叠。 * eg.非优化的aaaaa :-1 0 1 2 3 * How to get next[i] RECURSIVEly ? * p[i] == p[k] --> next[i+1] = next[i] + 1; * else --> let k = next[k], check again. *******************************/ #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; int* getNext(string p) { int l = p.length(); int* next = new int[l]; next[0] = -1; int i = 0, k = -1; while (i < l - 1) { while (k >= 0 && p[k] != p[i]) k = next[k]; i++, k++; if (p[k] == p[i]) next[i] = next[k]; // Enhancement. else next[i] = k; } return next; } int KMP(string t, string p){ int tlen = t.length(); int plen = p.length(); if (tlen < plen) return -1; int* next = getNext(p); int i = 0, j = 0; while (i < tlen && j < plen){ if (j == -1 || t[i] == p[j]) i++, j++; else j = next[j]; //重新对齐后,仍要比较一次i位置 } if (j == plen) return i-j; else return -1; }KMP的总比对次数:母串长度+失配次数
Examples of KMP:
index 0 1 2 3 4 5 string a b a c a b next -1 0 0 1 0 1/0 如何目测改进版Next数组:
先目测原始Next数组,之后逐位比较
p[i]==p[next[i]] ? next2[i]=next2[next[i]] : next2[i]=next[i].注意是next2[next[i]]。
eg.
index 0 1 2 3 4 5 string a a b a a c next -1 0 1 0 1 2 next2 -1 -1 1 -1 -1 (not 0!) 2 eg.
index 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 string a b c d a a b c a b next -1 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 3 1 next2 -1 0 0 0 -1 1 0 0 3 0
-
Boyer-Moore 算法
实际上Ctrl+F,GNU grep使用的算法,预处理O(m),平均查找O(n/m),最坏O(n),NB!
坏字符原则+好后缀原则。每次失配时,根据这两个规则中后移位数大的移动。
理解比较容易,但感觉在实现上有一些trick,所以不太适合教学。。?
http://blog.jobbole.com/52830/
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2013/05/boyer-moore_string_search_algorithm.html