mAP (mean Average Precision)
A metric usually used in object detection.
mAP = mean AP for all classes.
And the calculation of AP is like the AUC of ROC in binary classification:
AP
# for each class's `preds` and `gts`, assert both non empty.
THRESH = 0.5
matched = np.zeros(len(gts))
tp = np.zeros(len(preds))
fp = np.zeros(len(preds))
preds = sorted(preds, key="confidence", decreasing=True)
# for each pred
for i, pred in enumerate(preds):
max_iou = 0
max_id = -1
# brute-force enumerate gts of the same label!
for j, gt in enumearte(gts):
iou = get_iou(pred, gt)
if iou > max_iou:
max_iou = iou
max_id = j
if max_iou > THRESH and matched[max_id] == 0:
matched[max_id] = 1
tp[i] = 1
else:
fp[i] = 1
tp = np.cumsum(tp)
fp = np.cumsum(fp)
recall = tp / len(gts) # increasing
precision = tp / (tp + fp + 1e-6) # zig-zag
### VOC 2007 metric, calculate AUC on 11 discrete points.
ap07 = 0
for t in np.arange(0, 1.1, 0.1):
if np.sum(recall >= t) == 0:
p = 0
else:
p = np.max(precision[recall >= t])
ap07 += p / 11
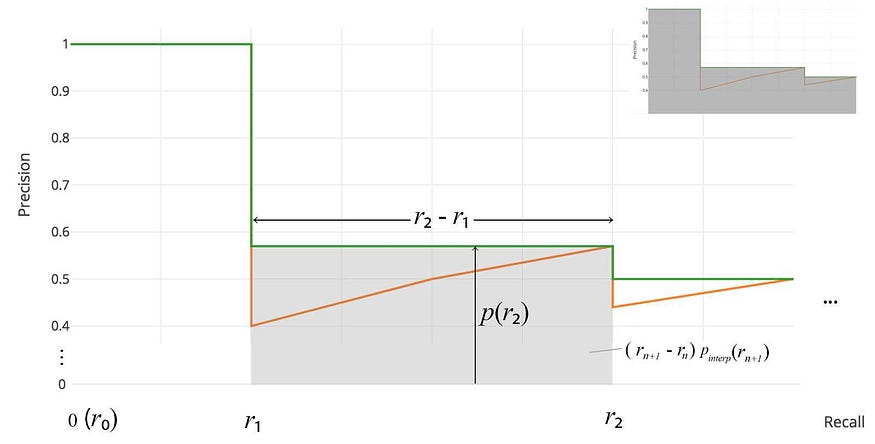
### VOC after 2007, continuous AUC
ap = 0
recall = np.concatenate([0], recall, [1])
precision = np.concatenate([0], precision, [0])
# smooth out the zig-zag
for i in range(len(precision)-1, 0, -1):
precision[i-1] = np.maximum(precision[i-1], precision[i])
xs = np.where(recall[1:] != recall[:-1])[0]
ap = np.sum((recall[xs + 1] - recall[xs]) * precision[xs + 1])
illustration of VOC 07:
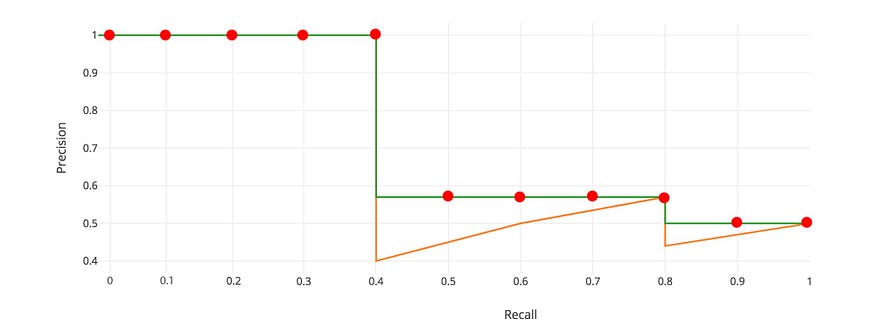
illustration of VOC after 07:
Other Notations
usually used in COCO dataset:
- AP@0.5: AP with threshold = 0.5
- AP@[.5:.95]: average AP (mAP) with threshold in
arange(0.5, 0.95, 0.05), the AP is not averaged on classes, but on the IoU thresholds.